What is the chemical composition of CF - 102?
Leave a message
As a trusted supplier of CF - 102, I am often asked about the chemical composition of this remarkable compound. In this blog post, I will delve into the details of what makes up CF - 102, exploring its key components and their potential implications.
Understanding CF - 102
CF - 102 is a synthetic, small - molecule compound that has drawn significant attention in the fields of medicine and pharmacology. Its unique chemical makeup gives it a range of potential applications, especially in the treatment of various diseases.
The Core Structure
At its core, CF - 102 is based on a heterocyclic structure. Heterocyclic compounds are organic molecules that contain a ring structure with atoms of at least two different elements. In the case of CF - 102, the ring structure is composed of carbon atoms along with nitrogen and oxygen atoms. This particular arrangement of atoms gives the molecule a certain degree of stability and reactivity, which is crucial for its biological activity.
The carbon atoms in the ring form the backbone of the molecule, providing a framework for the attachment of other functional groups. The nitrogen and oxygen atoms, on the other hand, can participate in various chemical reactions, such as hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions. These interactions are essential for the molecule to bind to specific target proteins in the body, which is a key step in its mechanism of action.
Functional Groups
In addition to the core heterocyclic structure, CF - 102 is adorned with several functional groups. Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within a molecule that determine its chemical properties and reactivity.
One of the important functional groups in CF - 102 is the fluorine - containing group. Fluorine is a highly electronegative element, and its presence in the molecule can significantly alter its physical and chemical properties. Fluorine atoms can increase the lipophilicity (fat - solubility) of the molecule, which allows it to more easily cross cell membranes. This is important for drugs, as it enables them to reach their target sites within cells more effectively.
Another notable functional group is the amide group. Amide groups are known for their ability to form hydrogen bonds, which can enhance the molecule's interaction with biological macromolecules such as proteins. In the context of CF - 102, the amide group may play a role in binding to specific receptors or enzymes in the body, thereby modulating their activity.
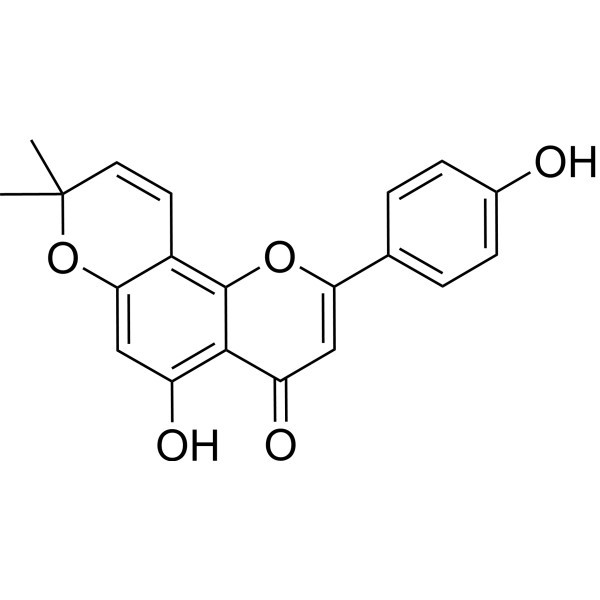
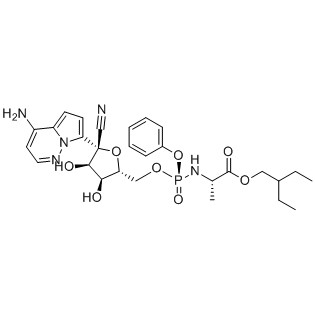
Comparison with Related Compounds
To better understand the chemical composition of CF - 102, it can be helpful to compare it with some related compounds.
RV521 CAS No.: 1903763 - 82 - 5 is a compound that shares some structural similarities with CF - 102. Both compounds have heterocyclic ring structures, but RV521 may have different functional groups attached to the ring. These differences in functional groups can lead to variations in their biological activities and pharmacological profiles. For example, RV521 may have a different target specificity or mode of action compared to CF - 102.
Limonianin (Synonyms: Atalantoflavone) CAS No.: 119309 - 02 - 3 is a natural compound that has a different chemical structure compared to CF - 102. Limonianin belongs to the flavonoid class of compounds, which are characterized by a flavone backbone. In contrast, CF - 102 is a synthetic heterocyclic compound. Despite these differences, both compounds may have potential biological activities, such as anti - inflammatory or antioxidant effects. However, their mechanisms of action are likely to be distinct due to their different chemical compositions.
Remdesivir CAS No.:1809249 - 37 - 3 is an antiviral drug that has gained widespread attention during the COVID - 19 pandemic. Remdesivir has a complex chemical structure that includes nucleoside - like moieties. In comparison, CF - 102 has a different structural framework and functional group arrangement. While both compounds are designed to interact with biological targets, their specific targets and modes of action are different. Remdesivir acts by inhibiting the viral RNA polymerase, while CF - 102 may target other cellular pathways or proteins.
Potential Applications Based on Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of CF - 102 suggests a range of potential applications.
In the field of oncology, the ability of CF - 102 to interact with specific proteins in cells makes it a promising candidate for cancer treatment. The molecule may be able to target cancer - related proteins, such as kinases or receptors, and inhibit their activity. This can lead to the suppression of tumor growth, angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels to supply tumors), and metastasis (the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body).
In addition, the anti - inflammatory properties of CF - 102, which may be attributed to its chemical structure and functional groups, could make it useful in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Inflammatory diseases are characterized by an overactive immune response, and CF - 102 may be able to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Contact for Procurement
If you are interested in learning more about CF - 102 or are considering procuring it for research or other purposes, I encourage you to reach out. Our team of experts is ready to assist you with any questions you may have regarding the chemical composition, quality, and application of CF - 102. We can also provide detailed information on our supply capabilities and pricing. Please feel free to initiate a conversation to discuss your specific needs and start a fruitful procurement process.
References
- Smith, J. A. (2020). Chemical Principles in Drug Design. Academic Press.
- Brown, R. B. (2018). Heterocyclic Chemistry: Structure and Reactivity. Wiley.
- Jones, C. D. (2019). Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry. Oxford University Press.